Definition of Class C power amplifiers:
A class C power amplifier is a high efficiency power amplifier. Where the transistor conducts for less than one half cycle (180°) of the input signal mostly active for less than 50% of the input cycle, meaning that they conduct less signal of the signal making it highly efficient but suitable primarily for applications where signal fidelity is not critical, such as RF (radio frequency) amplification. Maximax efficiency is nearly 90%
As we discussed in previous tutorials Fundamentals Of Amplifier, as well as class A amplifier and Class B amplifier but the class C amplifier provides more efficiency than others. This article focuses on the class C amplifiers, advantages disadvantages and tells you everything you need to know about it.
What is a Class C power Amplifier?
Due to more Ideal for RF applications and To give more efficiency than the Class A amplifier and class B amplifier so class C is referred.
These amplifiers require impedance matching and also need efficient cooling for heat management and harmonic filtering to prevent interference.
They are ideal for high-power RF applications where efficiency is important, such as cell phones, Wi-Fi devices, and radar systems etc.
The design considerations include frequency range, output power, and modulation schemes to optimize their performance in specific RF systems.
Working principle of class C amplifier:
A Class C amplifier’s functioning is focused on how to make good use of transistors. These amplifiers are especially ideal for high-frequency RF applications.
since they carry for less than half of the input cycle. Because of their fundamental non-linearity, they specialize at handling pulsed signals, which is a typical need in RF transmission.
While Class C amplifiers are highly efficient, they do generate harmonics that must be carefully filtered.
these amplifiers are used in RF applications like radios, cell phones, Wi-Fi devices, and radar systems due to their efficiency.
Operation of class C amplifier:
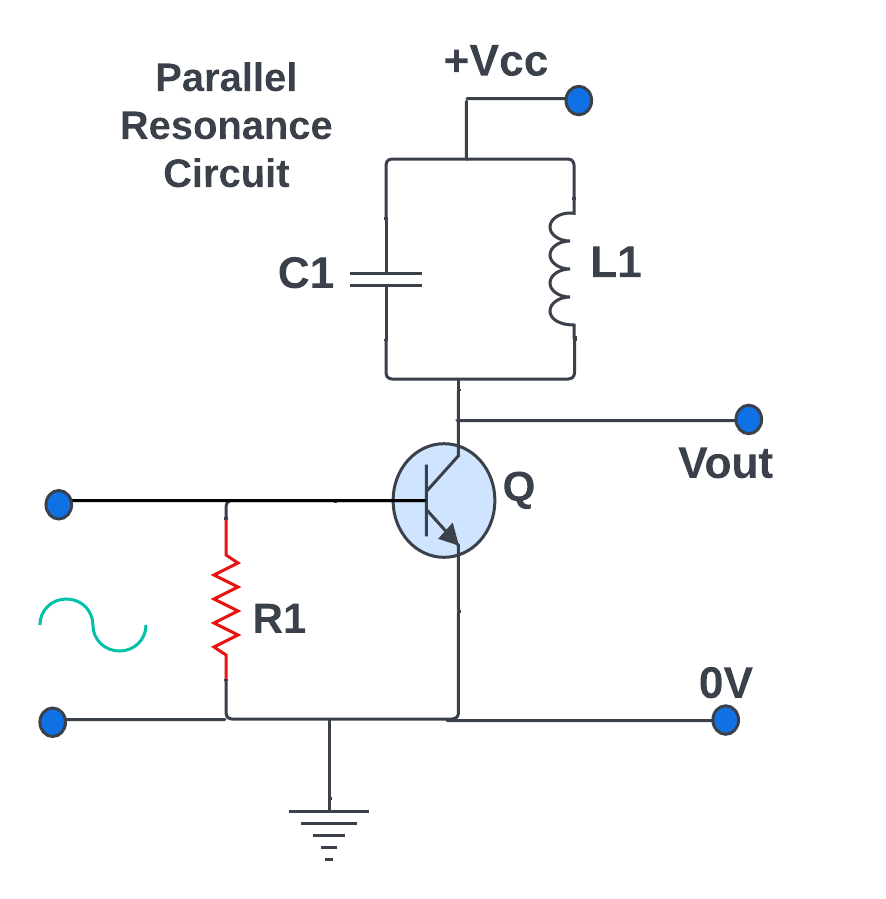
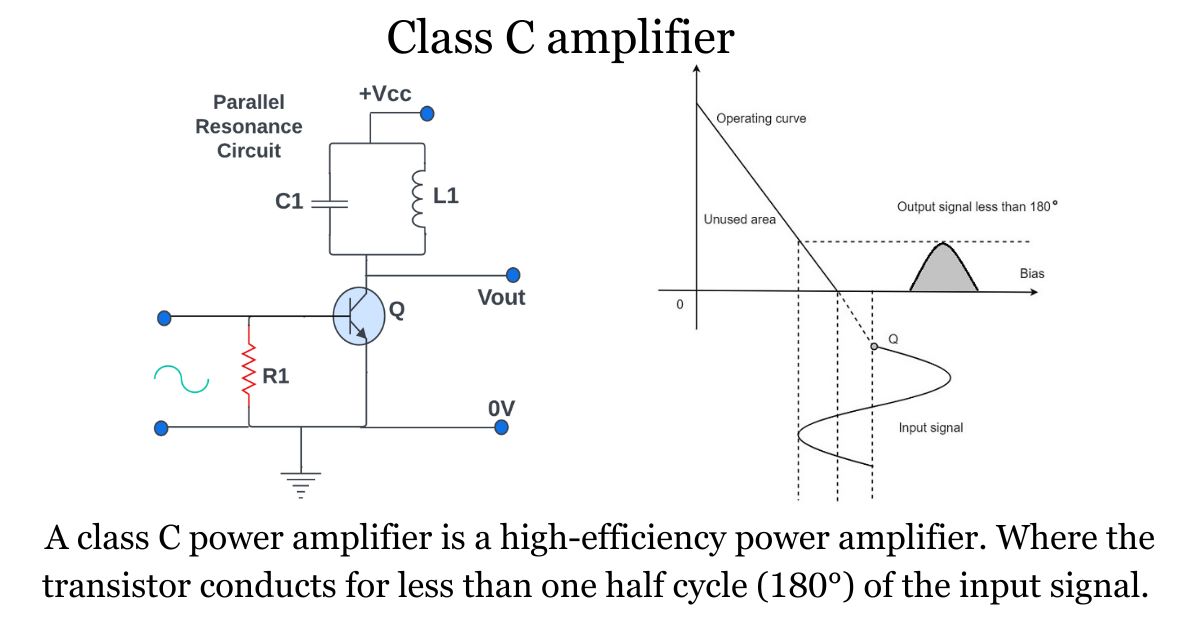
Circuit diagram of a class C amplifier It is the most efficient power amplifier. It is deeply bias so Q point is below to the cutoff region.
LC circuit is a resonant tank circuit for resonance frequency these circuit provide maximum output
Now it is the most efficient power amplifier, which is why it is called the most efficient power amplifier because the efficiency is higher than that of the class A and class B amplifiers.
Class C has a 95% efficiency, which means that whatever input is applied, 95% of the output is converted.
Since the efficiency is high, these amplifiers are called as most efficient power amplifiers. Now, to amplify the sinusoidal signal, it must be tuned to the sine signal frequency and because of that, it is also called Tuned amplifier so it will amplify the resonant frequency as well as the Closer to the resonance frequency.
For avoiding the large inheritance inductance and capacitance in resonance circuit we can use class c amplifier which will be Tuned to the resonance frequency as well it amplifies the radio frequency signal hence this amplifier is known as RF power amplifier. Bandwidth response is less compared to other classes.
Here is the NPN types of transistor are used with CE configuration the transistor Q is Bias with voltage Vcc.
To the Base-Emitter junction simply apply -Ve voltage at the output, connect the tank circuit these circuit must tune with input frequency to load resistance RL is connected to the tank circuit.
When applying signal input signal must be greater than bias voltage.
I/P Vin = Vbb+ VcutIn
Then only transistor Q will on and current will flow in circuit When the input frequency is equal to the resonance frequency, the amplified output is available at the tank circuit, and this output is given to the load resistor (RL). As in the circuit, a parallel tune circuit is used because of that impedance of the circuit is high.
The resonance frequency:
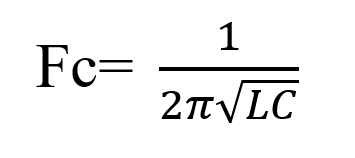
Where: L= inductor
C= capacitor
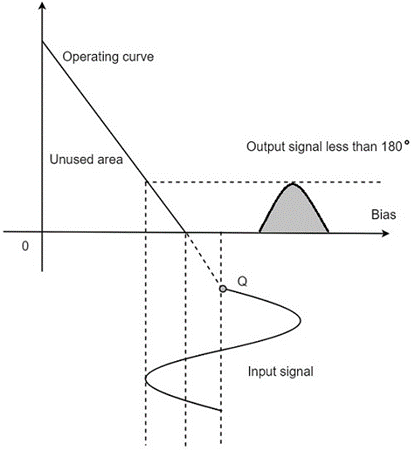
Q point is below to the cutoff X axis region point. That mean this amplifier is made to work below to the Q point, because of that it provides less conduction angle (600 to 120o) but it still has high frequency region for operation. This amplifier has good fly-wheel effect.
Characteristics of class C amplifier:
- Q factor is high
- Bandwidth is given as:
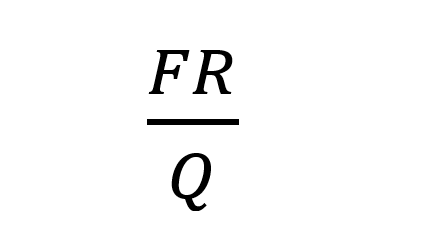
- Output current is flow during the positive half cycle of the input signal
- o/p is different from input signal
- most efficient power amplifier
features of class C amplifier:
- Q point is below to the cutoff region
- operated as high frequency
- conduction angle is less than 1200
- good efficiency near 90%
- not suitable for digital amplification
Class C power amplifier Output Characteristics:
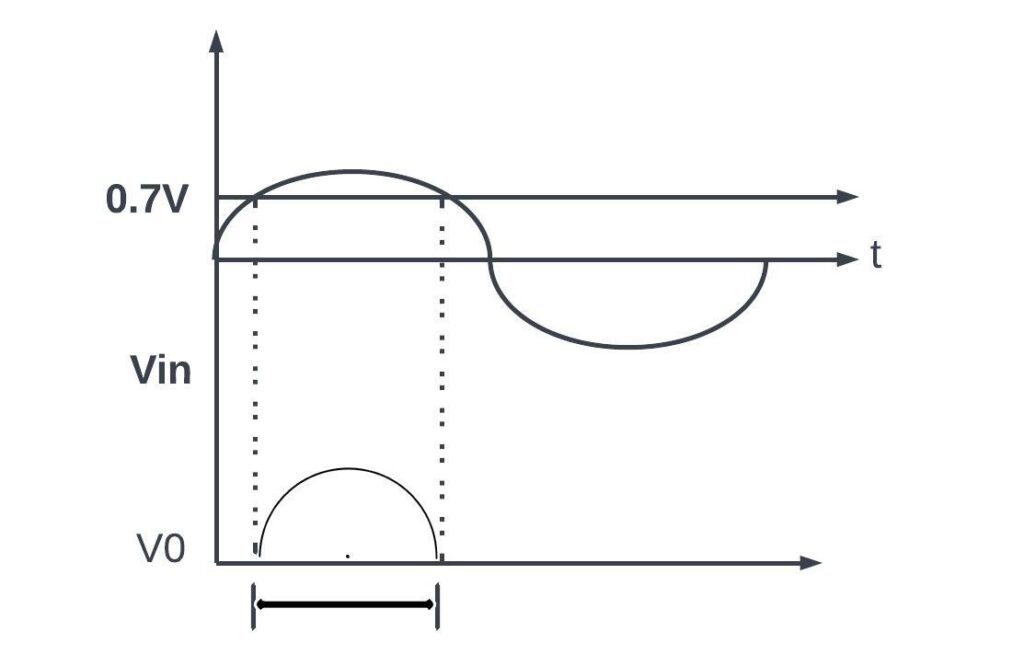
Case Ⅰ
for +Ve half cycle of Vin
Vin is 0.7 = Vin<0.7V
Q= Dose not conduct output
Case Ⅱ
For -Ve half cycle
Vb = -Ve
Q= Dose not conduct output
Case Ⅲ
For Q > 0.7V
Q= provide output
key formulas for Class C amplifiers:
1.Expression of the maximal value of the output current :
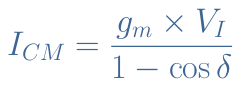
2.Efficiency of a class C :
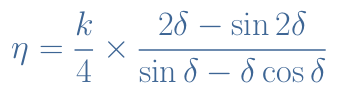
3.Frequency match relation :
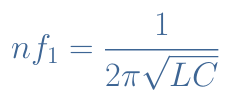
4.Output voltage :
Vout=Vsupply+k.Vsupply×sin(2πf1t+π)
Advantages of class C power amplifier:
- this type of amplifiers has very high efficiency
- it has Compact and lightweight design
- provide Low power dissipation
- class C amplifier is Suitable for RF transmission
- has Cost-effective
- generate very high-power output for load
Disadvantages of a Class C power amplifier:
- these amplifiers have High distortion
- it provides Limited applications
- the bandwidth is narrow
- not working at low power levels
- it is Difficult to design and match with loads
- class c amplifier has less linearity
- Limited modulation capability
- Heat generation is more
Applications of Class C power amplifiers:
RF transmitters: this amplifier class is used in AM (amplitude modulation) and FM (frequency modulation) for broadcasting purposes, as well as wireless communication systems and amateur radio for high-power RF signal generation.
RF Power Amplification: Class C amplifiers are used for RF power amplifiers for applications like radar systems and mobile communication base stations.
RF Modulation: Used in RF modulation circuits for AM and FM radio broadcasting and TV broadcasting.
Signal Generation: apply for signal generator circuits to generate high-power, high-frequency signals for testing and calibration.
RF jamming: radio frequency jamming such as military and security applications or to disable wireless communication signals.
Ultrasonic Applications: These amplifiers are Used in ultrasonic transducer driver circuits for ultrasonic sensors
Frequency Asked Questions [FAQs]:
Q. Is a Class C amplifier a linear amplifier?
Ans: A Class C amplifier is not a linear amplifier. It operates in a highly non-linear format.
This amplifier are primarily used for their efficiency in power amplification, particularly in RF transmission, where linearity is not essential.
Q. What is the frequency of Class C amplifier?
Ans: 1 MHz is the input frequency of this amplifier.
Q. Why is Class C highly efficient?
Ans: The Class C conducts less than half of the input cycle. Therefore, it is highly efficient.
Q. Which class amplifier is best?
Ans:
Class A:
Advantages: High linearity, low distortion.
Disadvantages: Inefficient, generates significant heat.
Class B:
Advantages: High efficiency.
Disadvantages: Crossover distortion at transition points.
Class C:
Advantages: Extremely high efficiency, often used in RF applications.
disadvantages: Not suitable for audio due to high distortion.
Class AB:
Advantages: Combines linearity and efficiency.
Disadvantages: Moderate efficiency.
Class D:
Advantages: Highly efficient, suitable for portable devices.
Disadvantages: May have higher distortion at certain frequencies.
The choice of amplifier class should align with your specific needs and design constraints.
Q. Which class amplifier is best for bass?
Ans: subwoofer amplifiers are class D because it gives high efficiency and significant power output also it is switched amplifier class.
Q. Where is a Class C biased?
Ans: It is biased below cutoff with the negative Source supply.
Summery:
In summary, a Class C amplifier is a sophisticated tool for efficiently boosting high-frequency RF signals. Its design makes it perfect for applications where power efficiency is a top priority, such as in RF transmitters and other devices that need to send strong signals without wasting energy.
Follow to the blog ETechSpark.com for more articles on electrical engineering, electronic and tech updates.
please leave your question in the comment section, give us your valuable feedback.