A flywheel diode also known as a flyback diode is a semiconductor device from voltage spikes generated by inductive loads when they’re turned off.
After Exploring PN Junction Diode’s– it’s applications now let us discuss the essential function of Flyback Diode or Freewheeling Diode.
What is freewheeling or Flyback diode?
A Flywheel diode is known by several different names in the engineering world, like Suppression Diode, Snubber Diode, Kickback Diode, and Clamp Diode, that demonstrating its adaptability and significance in a wide range of electronic applications.
Working of Flywheel Diode
A freewheeling diode, is a type of diode that used in electronic circuits for protecting components from voltage spikes that will occurs when an inductive load is being turned off like as motor or a relay coil etc.
This diode connected across the inductive load in reverse polarity. When the current to the load is suddenly interrupted, then freewheeling diode provides a safe path for the stored energy in the inductor to dissipate, that will prevent the damage to other components in the circuit it will be caused by the resulting voltage spike.
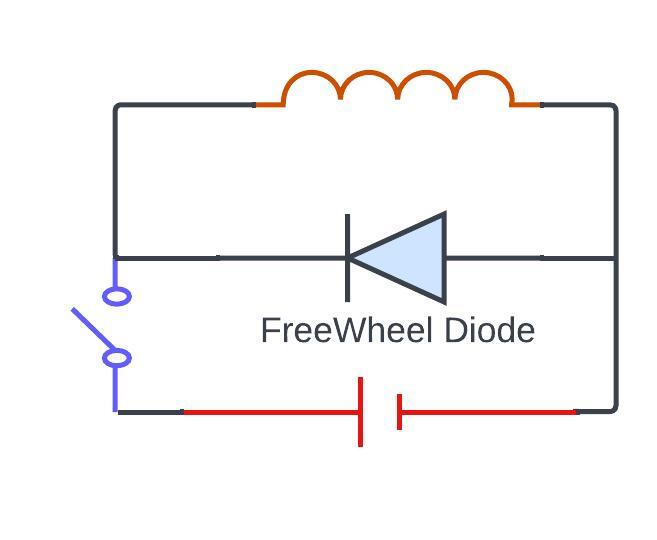
So, when we apply voltage to an inductor, it gets charges due to the dependence of its voltage on the changing electric current. However, upon halting the voltage, the inductor discharges, causing extra current in the circuit, resulting in additional power loss.
This discharge can also generate harmonics and disturbances, impacting the circuit’s stability.so, let’s discuss about what happens when the inductor discharges and how a free-will diode can make this operation simpler and easier
now we have to connect a DC voltage source to an RL load and in freewheel diode in parallel let’s see what happens
let’s suppose

V = DC voltage source
R = resistance
L = inductance
D = Diode
the moment when we connect then this battery to the inductor what happens is the current flows in a clockwise direction
however, if we draw the circuit the same circuit using a switch it looks like
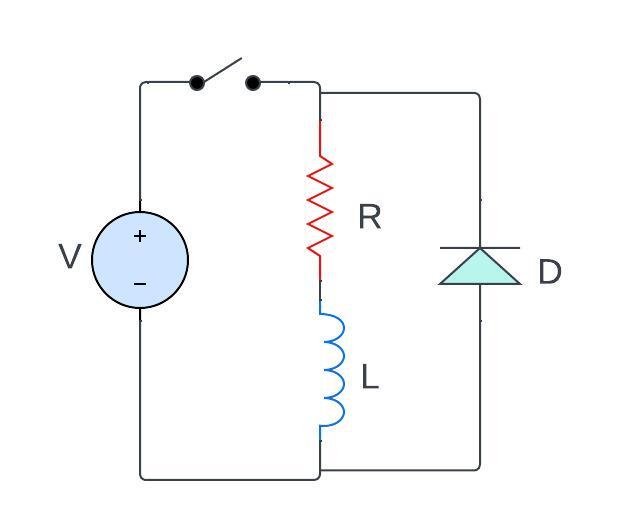
now if I close the switch the current starts flowing in the circuit in the loop to let, I be the current that is flowing through the circuit
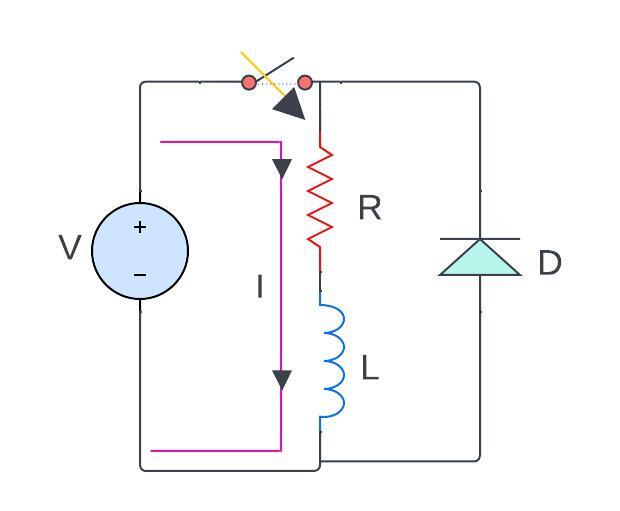
now when the current starts flowing inductor gets charged now if there is no diode here so when I close the switch electric current starts flowing in this loop
now let’s see what happens when I switch off this switch that means (open circuit) so after the inductor gets charged the switch become off now what happens is this becomes an open circuit the flow of electric current stops
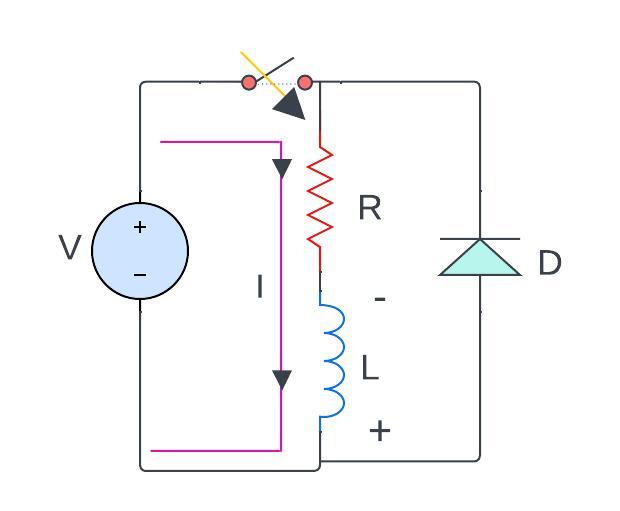
however, when the switch is again turned off the inductor changes its polarity because originally the polarity was this positive and negative because the current used to flow in the clockwise direction
if suddenly I switched this switch off or I keep the switch open what happens is the polarity across the inductor changes
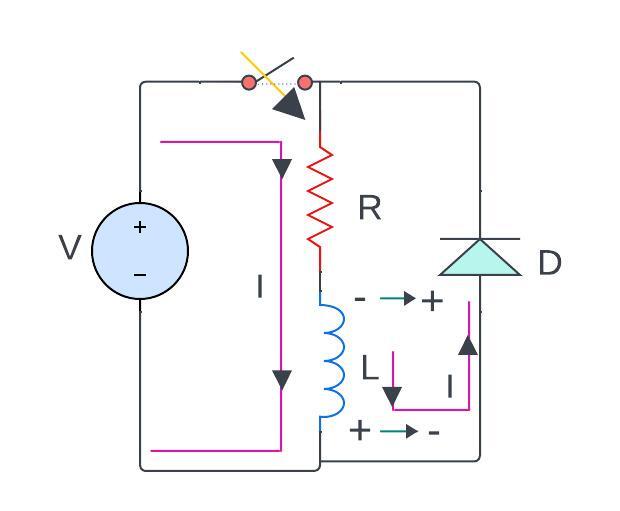
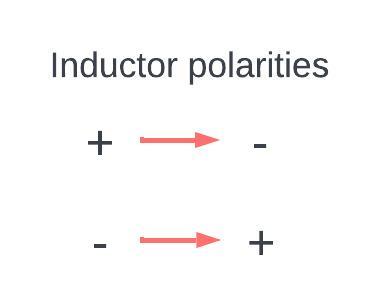
the discharging of inductor current now the current across the inductor
will be discharging in opposite direction
The key formula of freewheel diode is related to the energy stored in an inductor:
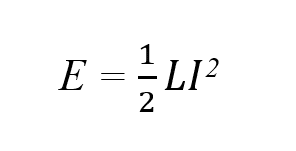
Where:
E is the energy stored in the inductor in joules(J)
L is the inductance of the inductor in henneries(H)
I is the current flowing through inductor in amperes(A)
Advantages of freewheel diode
one of the major advantages is that
It provides a path for that discharge current
it is current so friends using a freewheel diode is same as using a flyback in a motor so freewheel dad for that reason is called a flyback diode
because it provides a path for the discharge which is highly beneficial for the circuit because if we do not provide a discharging path for the inductor or a capacitor the circuit might get destroyed because of over current or because of extra harmonics
because of the freewheel diode it creates a complete path for the discharge current which prevents from the overcurrent
protection which prevents for the harmonic to be introduced in the circuit and finally this is very important for the safety purpose as well
Why freewheeling diode is used?
- Relay Driver
- H- bridge motor drivers
- Full wave rectifier
- For protect circuits from damage caused by sudden interruptions
- They work with components like relay coil or motor windings to handle strong counter EMF.
- These diodes ensure a smooth path for current during interruptions, preventing harm to sensitives parts.
What is the purpose of the flywheel diode?
- Boosting the cd voltage by adjusting the firing angle in SCR phase-controlled converter eliminates negative waveform potation.
- This reduction in negative segments lessens the generated rippled voltages on the converters DC side.
- Improving the input power factor (pf) in SCR phase-controlled converter occurs because it allows the input current waveform to conclude earlier, facilitating internal freewheeling.
What causes Flyback?
- The primary causing reason of Flyback is because of electromagnetic induction
- Capacitors resist sudden changes in voltage by either drawing or supplying current to balance the voltage changes.
- Inductor resist changes in current flow by creating a voltage that linked to how fast the current changes
What is another name for a Flyback diode?
There are several names of Flyback diode which as follows –
- Freewheeling diode
- Snubber diode
- Catch diode
- Suppression diode
What is the difference between diode and freewheeling diode?
As we discussed in our pervious tutorials you can get more idea from that tutorial so basically A diode is like an electric valve that lets current flow in one direction only. It stops the flow in the opposite direction.
Now, a freewheeling diode is a special kind of diode. They can make a kind of electrical; backlash that might harm the circuit. The freewheeling diode gives this extra electricity a safe path to flow through, protection the circuit from damages.
Why Flyback for low power?
Using a flyback setup for low power well because it simple, cost-efficient and suit smaller devices. Its efficiency with smaller components and fit the needs smaller electronics where space matter.
Frequently asked questions
Q. Can freewheel diodes be used in DC circuits?
Ans: Yes, freewheel diodes can be used in both AC and DC circuits with inductive loads to protect against voltage spikes.
Q. can Flyback diode fail?
Ans: like any electronic components, flyback diode can fail due to overvoltage, overcurrent or exceeding their voltage and current rating. Proper selection and instilment are the crucial points for their maintain reliability.
Q. Are freewheel diodes always necessary?
Ans: see they are essentials for circuits with inductive loads to prevents voltage spikes and protects the components. However, in some cases, the circuits design might incorporate other methods like snubber circuits to achieve similar results.
Q. what are the types of freewheel diodes?
Ans: Freewheel diodes can be standards silicon diodes or a specified diodes like Schottky diodes or fast recovery diodes, chosen based on the applications specific’s requirements.
Q. do freewheel diodes have any limitations or drawback?
Ans: while freewheel diodes are effective in protecting circuits, they can introduce voltage drops and power losses due to their Forward voltage drop when conducting.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the freewheel diode stands as a critical component in electronic circuits, enabling the smooth flow of current and preventing damages to sensitive components. Its ability to dissipated stored energy effectively, regulate voltage spikes and maintain circuit integrity that is make it indispensable in various applications.
Follow to the blog ETechSpark.com for more articles on electrical engineering, electronic and tech updates.
please leave your question in the comment section, give us your valuable feedback.