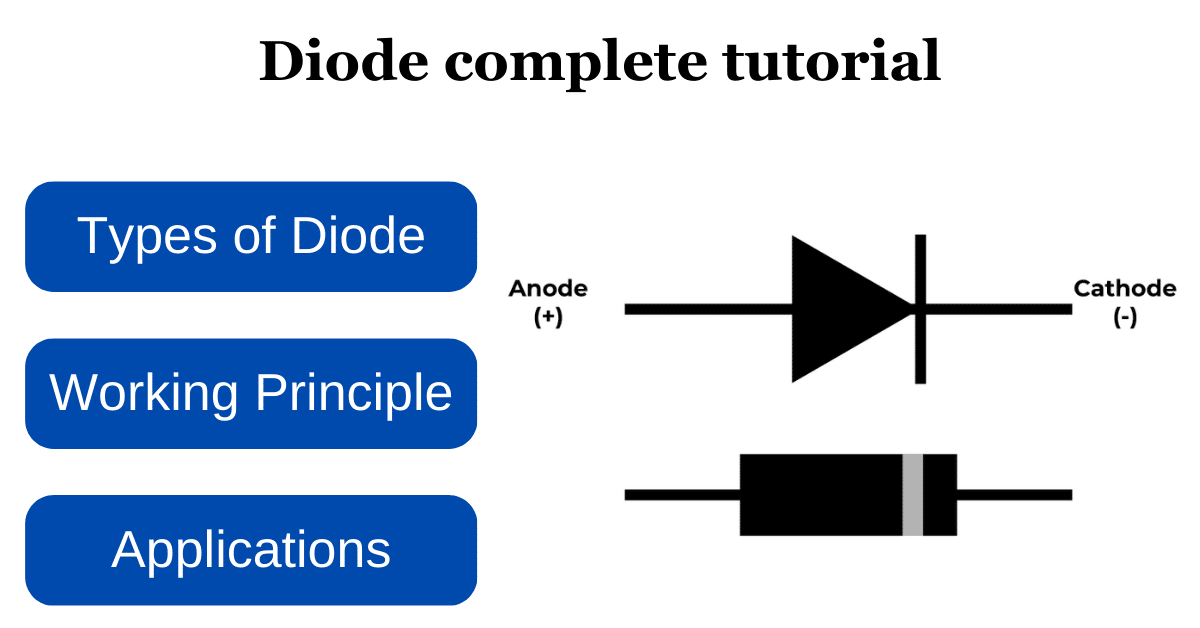
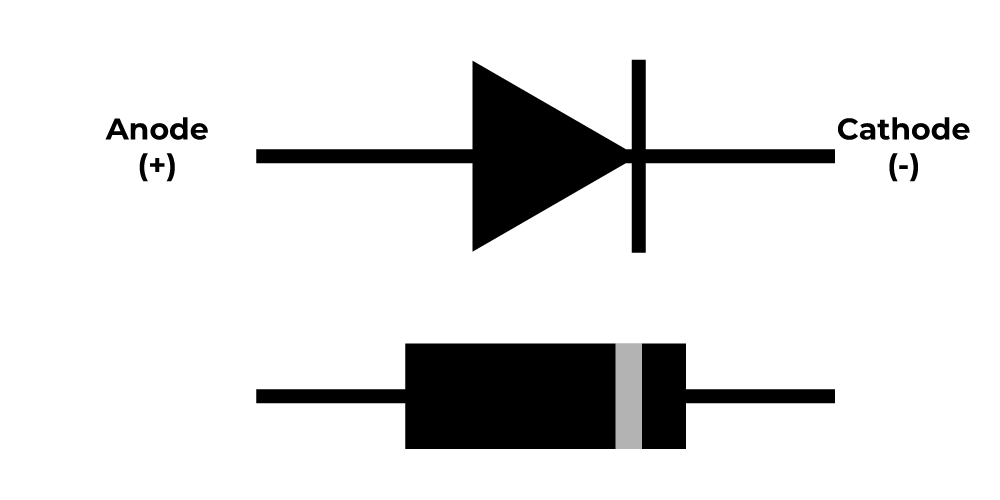
A diode is a semiconductor device that permits current to flow in one direction while blocking it in the opposite direction. It consists of two materials that are anode and the cathode.
when a positive voltage is applied to the anode (+) with respect to the cathode (-), so it allows current to flow easily it act like a closed switch however if the voltage is applied in the opposite direction The diode act as an open switch preventing the flow of current diodes are a fundamental component in various electronic circuits used for rectification, signal modulation, voltage regulation and many more.
In this article we will study what is diode? its working principle and various applications of diodes.
working principle of diode?
Brief overview of diode and their significance in electronics
Diodes are fundamental components in electronics, these are two terminal semiconductor devices crucial for controlling the flow of electrical current. This primary function involves allowing current to pass in one direction while blocking into the opposite direction, these are traits essential for rectifying alternating (A.C.) into direct current (D.C.) and this process is called as rectification.
Diodes also have an important role in voltage regulation. Zener diodes are maintaining a consistent voltage role in voltage regulation. It can maintain a consistent voltage level in circuit, that’s providing safeguarding for sensitive components against power fluctuation therefore it is used as a voltage regulator.
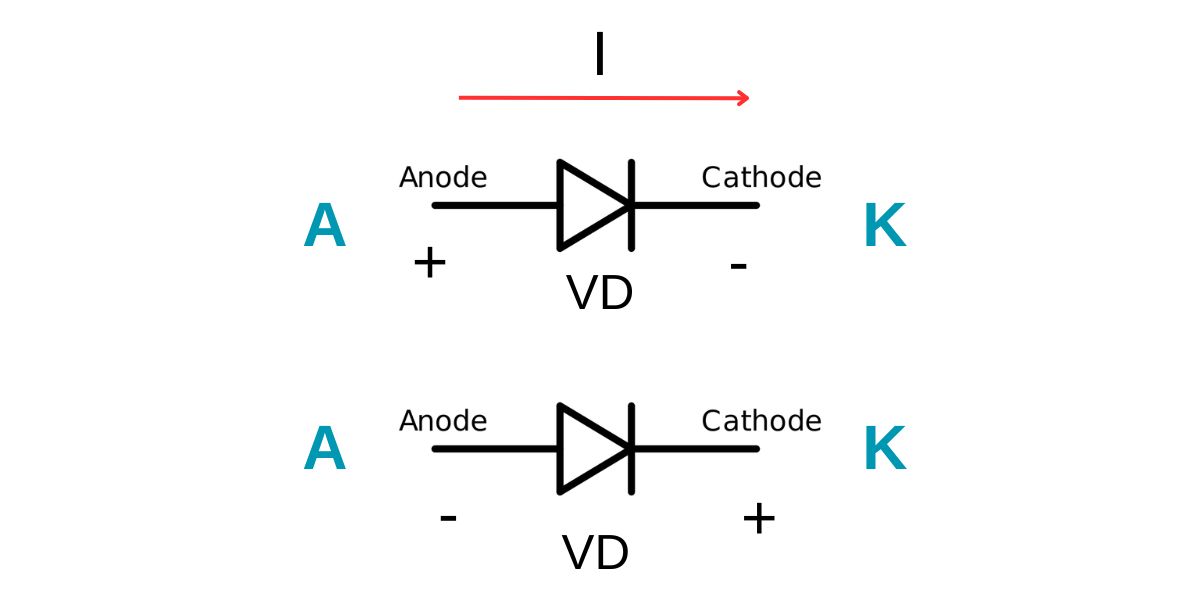
Definition of Diode
Diode is defined as two terminal electronic components that pass current in only one direction and block in the opposite direction.
Most of the diodes are used for safety purposes in electronics circuits. A diode will have negligible resistance for the conducting direction so, it allows current to flow and in the reverse manner it has high resistors. it uses for reverse direction to prevent the current flow. a diode efficiently like as a valve in electrical circuits that flow current in one direction only.
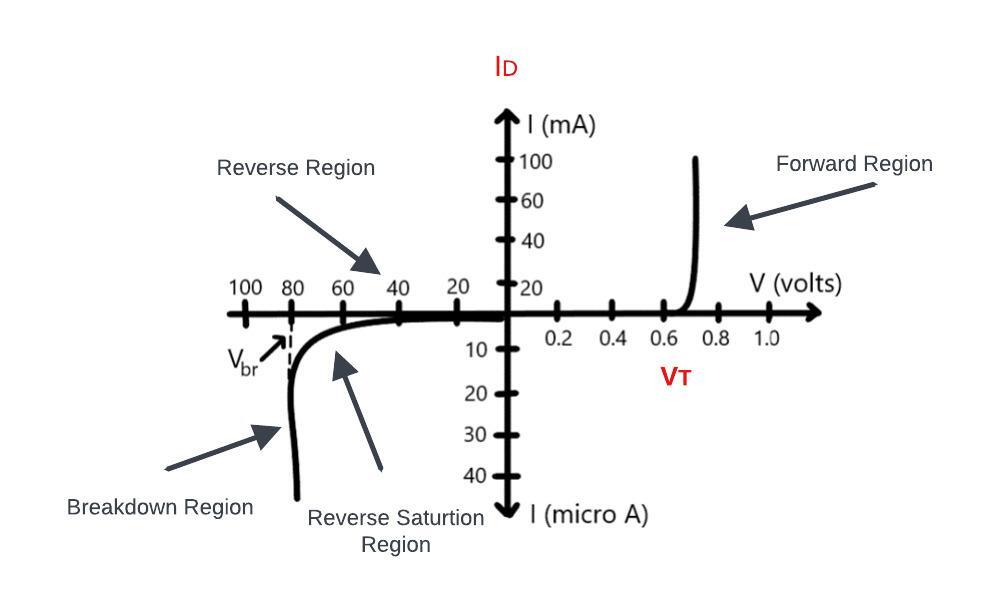
Understanding Diode V-I characteristics
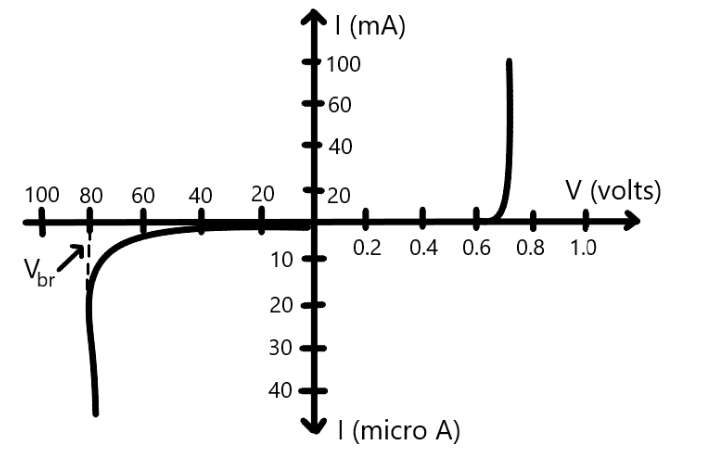
Diode V-I Characteristic Curve explaining forward and reverse bias region. The relationship between the voltage and current for the diode is non-linear. Now, if we look at this graph, then it looks like, the graph is symmetrical in both directions. But don’t get confused by the symmetricity, because here in this graph, both positive and the negative axis has a different scale. On the positive Y-axis, we have a scale in milli-ampere. While on the negative Y- axis, we have a scale in microampere
what is Ideal Diode
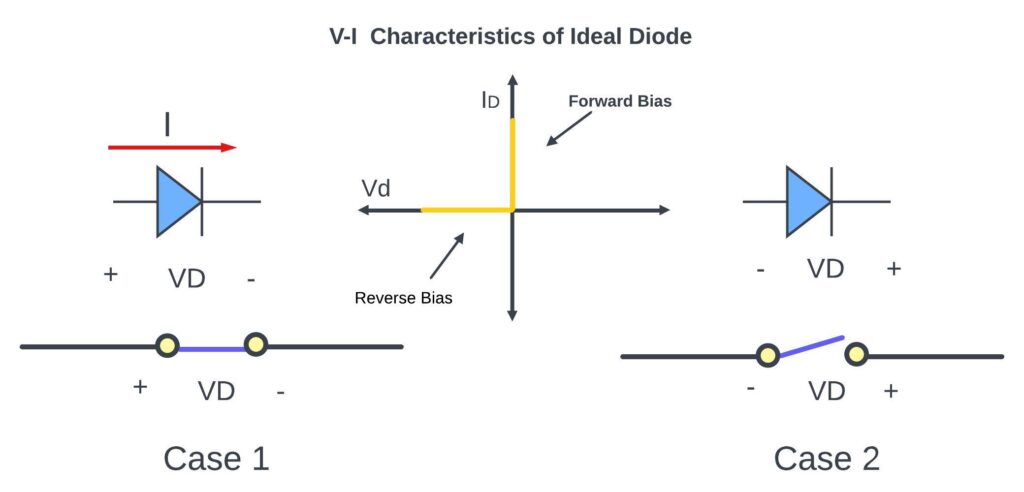
for this ideal diode, we will see the V-I characteristics. And also we will see the equivalent circuit for this ideal diode.
For the ideal diode, whenever the voltage that is applied between the anode and cathode is positive, then simply it will act as a closed switch. On the other end, if the voltage that is applied between this anode and cathode is negative, in that case simply it will act as an open switch.
So, now let’s see the V-I characteristic for this ideal diode.
Let’s consider the two cases
Case-1:
when the applied voltage is positive (+Ve)
on the V-I characteristic we will get the vertical line.
Case-2:
when the applied voltage is negative (-Ve)
then, for that case, we will get the horizontal line on the negative x-direction.
So, here is the V-I characteristics for the ideal diode
Threshold Voltage
The Threshold voltage in a diode refers to the minimum voltage required to make the diode conduct electricity (current) in the forward direction. Below this threshold voltage the diode acts as an insulator and does not allow significant current flow on the applied forward voltage. Exceed this threshold the diode starts conducting and gives permit to current flow through it.
V-Characteristics, then it will look like this.
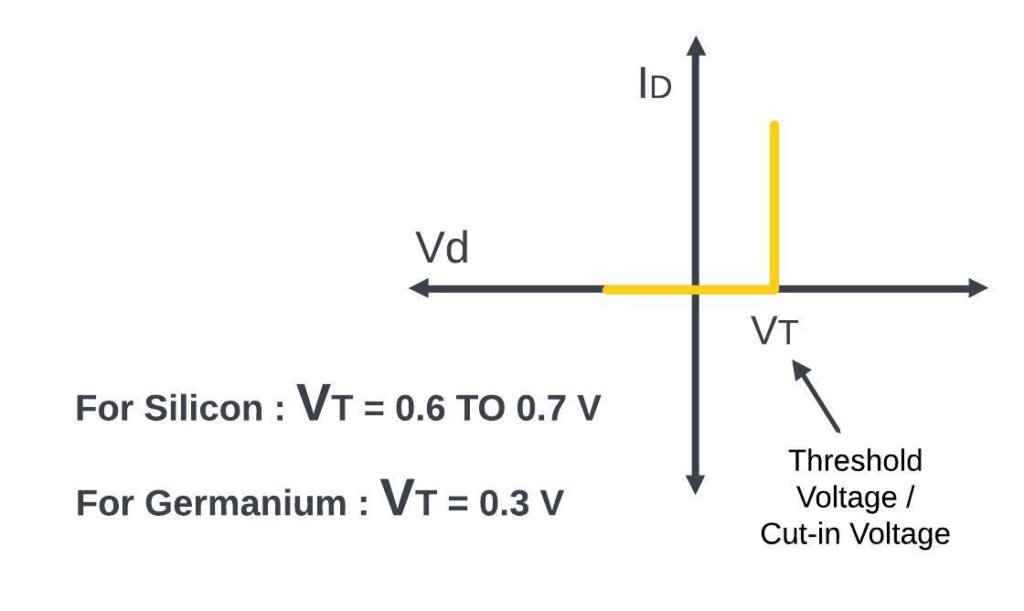
So, this voltage is known as the threshold voltage or the Cut-in voltage for the diode.
And usually, it is made of either silicon or germanium. So, for silicon, this threshold voltage used to be in the range of 0.6 to 0.7 V. While for germanium usually, it is around 0.3V. So, the diode will start conducting once the applied voltage crosses this threshold voltage. And before that, it will not allow any flow of current.
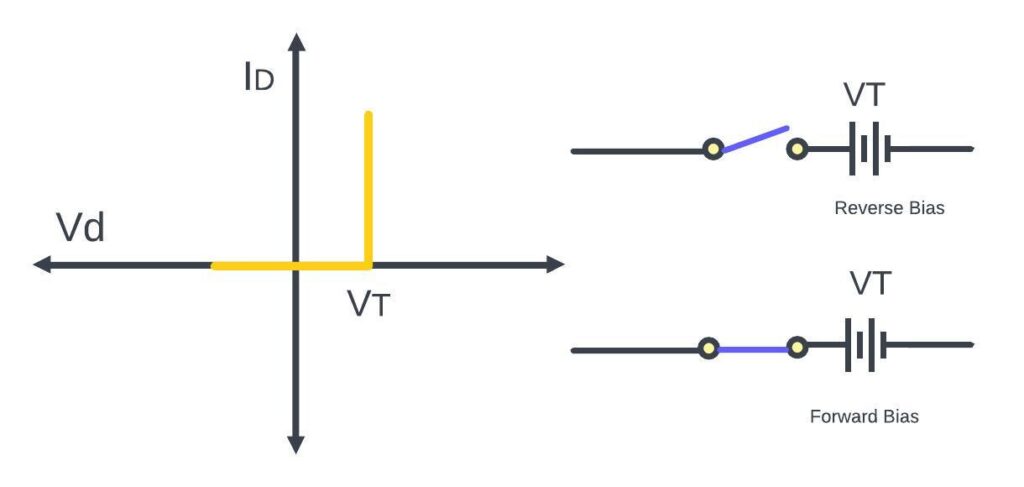
If the voltage under the threshold so then diode act as a open switch and doesn’t allow any current and whenever they voltage above the or process the threshold level then diode act as a close switch and passes the current
piecewise linear characteristics of Diode
We have segmented the actual characteristics of this diode into the piecewise linear characteristics. So, up to the threshold voltage, we have assumed that the diode is non-conducting. And after the threshold voltage, it will offer some finite resistance.
Forward reason:
the forward bias in diodes occurs when a voltage is applied across the diode in a way that allows current to flow from the p-type semiconductor to the N-type semiconductor.
Reverse reason:
In Reverse bias the width of the depletion Reason is increased that creative barrier to the flow of current as result only a small leaked current typically negligible current passes through the diode in Reverse bias
Breakdown region:
The Breakdown region in a diode is where under a reverse bias, a sudden surge in current happens due to the breakdown of the diodes insulating properties.
What is p-n junction diode and its working
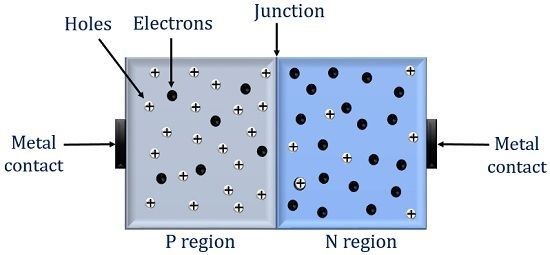
Basic structures of diode
A Diode consists of two semiconductor materials one with an excess of positive charge carriers that is P type and other one is an excess of negative charge carriers that is N type these both form a PN Junction. When these materials are joined, they create a boundary where electrons and holes recombine and form a depletion region that restricts the flow of current in the absence of an external voltage. applying a forward voltage allows it to flow by reducing this barrier while a revers voltage widens the barrier, preventing significant current flow.
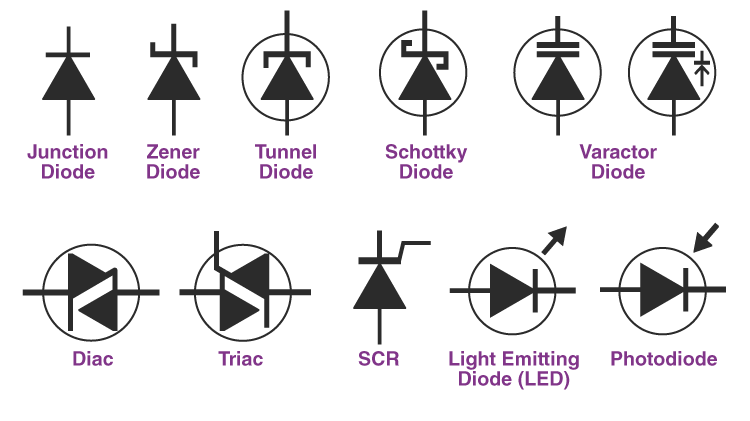
What are the Types of diodes
Rectifier diode:
Rectifier diode is primarily used for converting alternating current AC to direct current DC it a lost the current flow in One Direction while blocking in the opposite direction
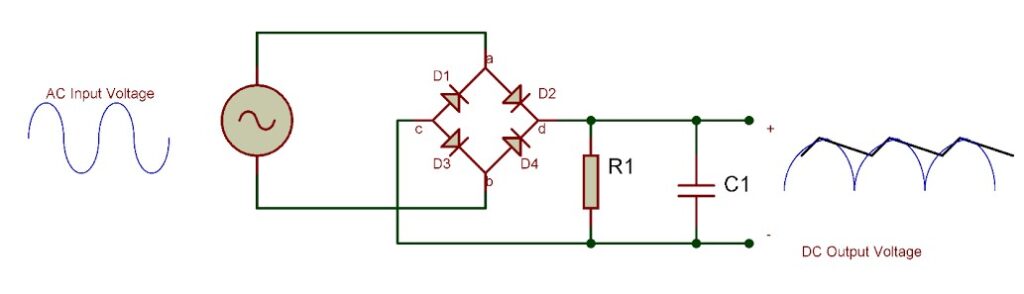
There are two types of rectifier diodes
1.Half wave rectifier
Half wave rectifiers allowed only half wave of AC waveform to pass resulting in a pulsating DC output.
2.Full wave rectifier
Full wave Rectifier mostly found in bridge rectifier configurations that converts both half of the AC waveform into more constant or smoother disable form.
Zener diode:
Zener diode is a semiconductor device that conducts for both buyers especially for reverse bias when a specific voltage that is inner voltage is reached, it offers stable voltage regulation and protection in electronics circuits.
light emitting diode:
A light emitting diode (LED) Is a device that emits light when an electric current passes through it commonly found in various applications like; lighting, displays, indicators and many more because it has a good efficiency, durability and it can produce different colours.
Schottky diode:
A Schottky diode Is a semiconductor diode that features a metal semiconductor Junction, that is known for its fast-switching speed and low forward voltage drop. This diode is used in such applications where high frequency is required, also used for rectifications and voltage clamping devices because of its unique characteristics.
Varactor diode:
Is a semiconductor device that functions as a voltage controlled variable capacitor. This diode is also known as voltage variable capacitor or vari-cap diode. It is commonly used for tuning circuit phase locked loops and frequency modulator.
Applications of diode
here are some applications of diodes-
Rectification: converting AC to DC power supply
Voltage regulation: uses in a diode for stable voltage output
logic Gate: for building blocks in digital circuits
frequency control: varactor diode for tuning circuits and phase-locked loops.
Protection: Provide protection from rivers polarity and voltage spikes to the circuit
light emission: LED for lighting indicators and displays.
microwave applications: for high frequency operations the Schottky diodes are used
Frequently asked questions
Q. Do diodes work on AC or DC?
Ans: Diode can be works for AC also for DC since it is a unit directional device that allow current to pass only one direction if the diode is used in AC so it will conduct only during the half of the cycle does their used to conversion of AC into DC and is known as rectification
Q. Is Zener diode AC or DC?
Ans: Primarily Zener diode used for voltage regulator to maintain a constant voltage and it used as a voltage regulator in D.C. circuits.
Q. Is diode a rectifier?
Ans: A diode is used as a one-way directional switch and a rectifier is convert AC into DC power supply so the rectifier must be consisting diodes.
Q. What is known as a rectification?
Ans: Rectification Is a process where the electrical devices convert alternative current AC into direct current DC and for that diodes are used.
Q. What is a rectifier example?
Ans: A popular example of rectifier is in mobile phone charger also it is found in receiver in radio system, diode tubes in vacuum cleaner junction diode etc
Conclusion
Diodes are fundamental Semiconductor devices with versatile applications across various fields. They serve a crucial role in rectification, regulation, signal processing and protection. Diodes used in modern electronics for enhancing the technology.
Follow to the blog ETechSpark.com for more articles on electrical engineering, electronic and tech updates.
please leave your question in the comment section, give us your valuable feedback.