Definition of electrical motor
An electrical motor is a device that transform electrical energy into mechanical motion. It operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction it has a coil or armature generating a magnetic field when exposed to an electric current.
This interaction between magnetic fields induces movements and this movements makes electric motors crucial for various applications from everyday appliances to industrial machinery.
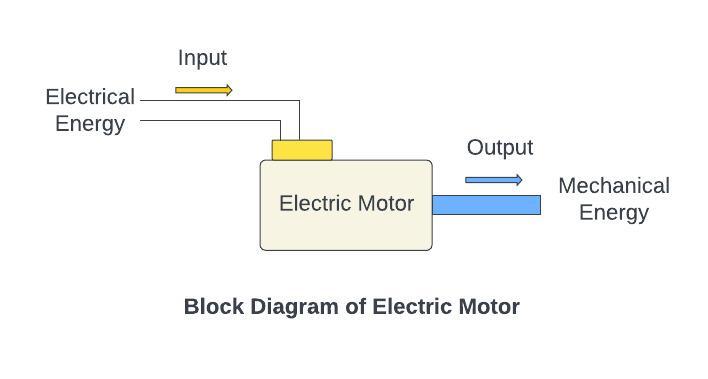
Block diagram of Electrical Motor
Working Principle of An Electric Motor
An electrical motor operates based on the fundamental principle of converting electrical energy into mechanical motion through the interaction of magnetic field.
In the motor’s construction there are stationary magnetic field is established in the stator, which can be created using permanent magnets or electromagnets. This magnetic field serves as a foundation for the motors functionally.
Within the motor there is a component that known as rotor that is capable to rotate and it consist wires. When an electric current is flow through this coil so it transforms into an electromagnet. The key intersection occurs as the magnetic fields of the stator and the rotor coil interact, that leads to generate the Lorentz force and this force is crucial in initiating the rotational motion of the rotor.
The rotational motion is sustained by the continuous generation of electromotive force (EMF) in the coil as it rotates. This induced EMF ensures that the current flow persists and maintaining the rotational momentum of the motor.
As further the working of the electrical motor has the ability of the motor convert electrical energy into mechanical motion makes it a versatile and widely used components in various applications.
Working Principle of DC Motor
In the case of direct current (DC) motors an additional mechanism involves the use of a commutator and brushes. These components play a crucial role in reversing the direction of the current I the rotor coil as it rotates.
This reversal is essential to maintaining a consistent and controlled rotational directional of the motor. While variations exist in motor designs and control mechanisms. The overarching principle of magnetic field interaction with a current-carrying conductor remains a constant in the operating of electric motors.
Types of Electric Motors
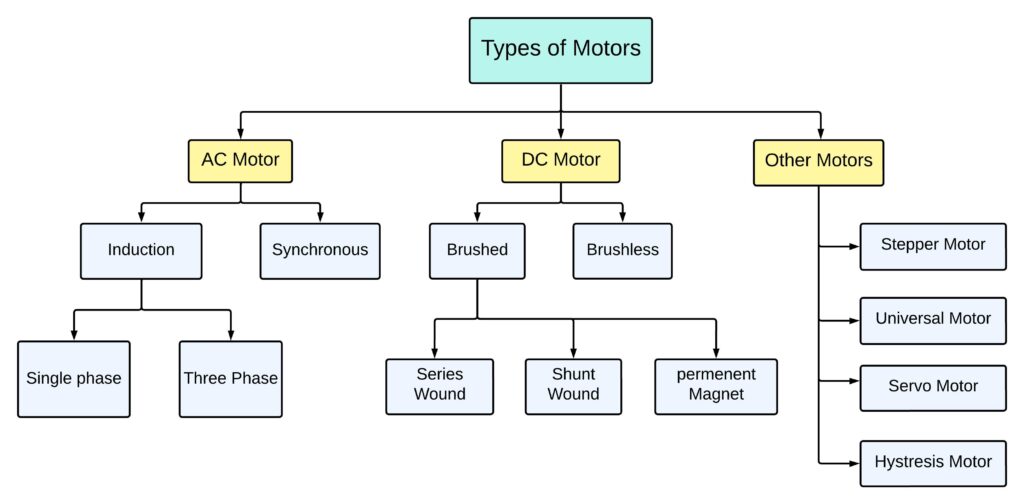
There are various types of electrical motors each designed for a specific application here are some common types of motors as follow:
DC Motor:
Brushless DC Motor: these motor use brushes and a commutator to switch the direction in the rotor windings.
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC): BLDC motor use electronic controllers instead of brushed and commutators for more efficient and maintenance free operations.
AC Motor:
Induction Motor: these motors operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction and are widely used due to their simplicity and reliability.
Single-phase Induction Motor: this motor typically used in household applications.
3-phase induction Motor: commonly employed in industrial applications.
Synchronous motor: these motors rotate at a constant speed synchronized with the frequency of the applied AC power.
Special purpose motor –
Servo Motor:
this motor deigned for precise control of position and speed. They are commonly used in robotic and automation.
Steeper Motor:
A stepper Motor can move in discrete steps that making them suitable for applications which required precious control of rotation such as printing and CNC machine etc.
Hysteresis Motor:
These motors use the hysteresis of magnetic material to generate motion in motor. This motor is known for their smooth and quite operation.
Linear Motor:
Instead of rotational motion here is the linear motors produces linear along a straight path. A linear motor has applications in high-speed transportation systems and manufacturing.
Universal Motor:
Designed to operate on either AC or DC power. universal motor are often used in devices like power tools and small household appliances.
Geared Motors:
A motor with integrated gear mechanisms for applications requiring low-speed but high-torque for output these types of motor are found in electric vehicle or robotic arms etc.
Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
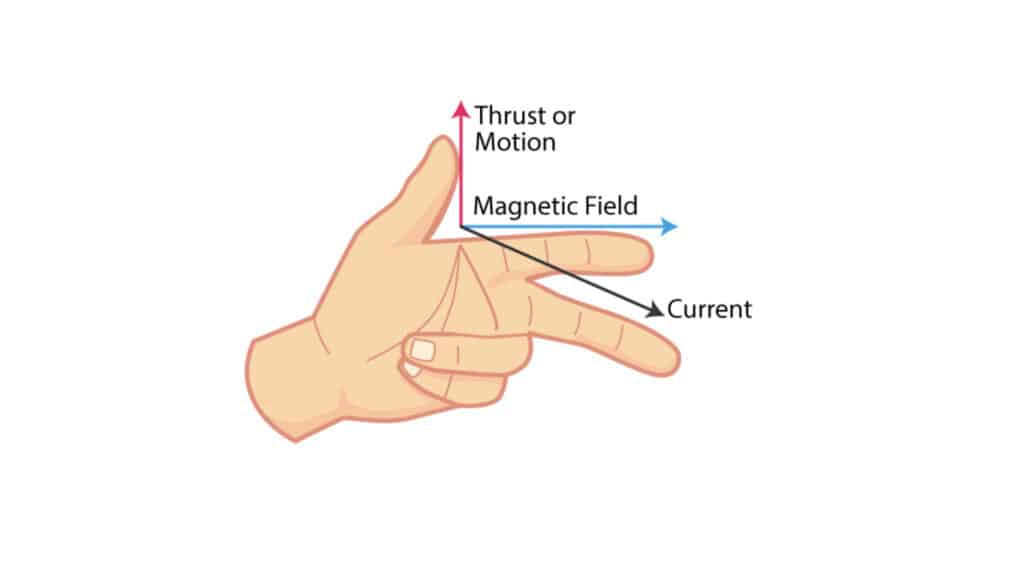
A Fleming’s Left -Hand Rule state that hold your left hand with your thumb, forefinger and middle finger that forming a right-angle when:
- Thumb (T): that represents the direction of the force (motion)
- Forefinger (F): represents the directions of the magnetic field
- Middle Finger (M): represents the directions of the electric current.
Now, think about how these directions interacts
- When the magnetic field (F) and the current (M) are at right angle then the resulting force (T) will be perpendicular to both.
- This interaction causes the coil to rotate. The motor uses this rotation to do work like turning a fan or spinning the wheel of an electric car.
Construction of Electric Motor
Let us see the Construction of Electric Motor One by one
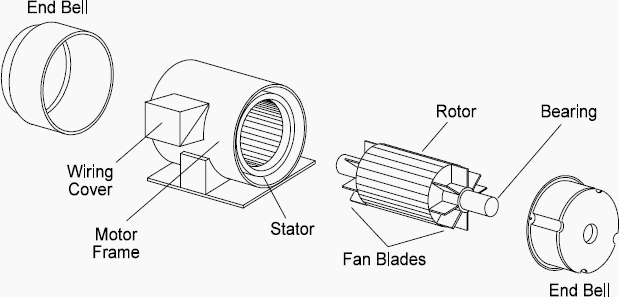
An electric motor consists of a coil of wires that called as a armature this armature placed between two magnets. When electric current flows through the coil so it creates aa magnetic field that interacts with the magnets that will causing the coil to spin and generate mechanical energy.
Parts of the Electric Motors
To achieve a decent working of electrical motor we should know the parts of the motor, here are the main components a parts of the electrical motor
- Stator:
The stator is the stationary parts of the motor and that typically consist of a core made of laminated iron sheet.
It houses the coil or winding that are connected to the power source. When current flows through the coil so it creates a magnetic field in the stator.
- Rotor:
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor and is located inside the stator. It usually made of a series of conductive bars or coil connected to the power supply through brushes or a commutator.
- Winding or coil:
These are wiring coil wound round the stator poles. When electric current flows through these coils this coil generates a magnetic field.
The arrangement and design of these windings contributes to the motor’s efficiency and performance.
- Commutator (in DC Motor):
If we look a working of direct current (DC) motor commutator plays major role. The commutators are a rotary switch that reverse the direction of the current in the rotor windings, ensuring a continuous rotation. It consists of segments and brushes that maintain electrical contact with the rotor as it turns.
- Brushes (in DC motor):
A brushes in electrical motor are made of carbon and are in contact with the commutator in DC motor. They conduct electric current between stationery and rotation parts of the motor.
- Bearings:
Bearings are used for support to rotor and allow it to rotate smoothly within the stator. A bearing is mainly used for reduces the friction and wear, it contributing to the motor’s overall efficiency.
- Shaft:
The shafting is attached to the rotor and extended outside the motor. Shaft are used for transfer the rotational motion to other mechanical components like as a fans, pumps or wheels.
Applications of Electrical Motor
As we know applications of electrical motor in wide range across various industrials and everyday life. Here are some common applications of electrical motor.
Industrial Machinery:-
Manufacturing equipment’s –
An electrical motors are used in various manufacturing processing such as conveys belts, assembly line systems and robotic arms etc.
Pumps and compressors –
Motors power pumps for fluid transfer and compressors for air or gas compression in industrial setting.
Robotics:-
A servo motor and steeper motors are used for joints and movement’s purpose in robotics for achieving specific applications.
Transportation:-
Electrical Vehicles (EVs) –
Electric motors are the primary propulsion sources in electric cars, buses and bikes.
Trains –
Applications of electrical motor are found in trains are used in locomotives and light rail systems.
Ships –
Motors power electric propulsion systems in some modern ships.
Home Appliances:
Kitchen Appliances –
Motors are found in blenders, food processors, mixers and coffee grinders also found in laundry appliances motor drivers washing machines and dryers.
HVAC Systems –
These motors are uses in fans and compressors in heating, ventilations, and air conditioning systems.
Power Tools:
An AC and DC motors are used in a various power tool such as drilling, saws, grinding and many other purposes.
Medical Devices:
A various types of motor are used in such medical equipment includes pumps, dental drilling and diagnostic devices.
Various applications of Electrical motors such as –
- Consumer electronic – for DVD players, CD players etc.
- Aerospace – including landing gears, fuel pumps also utilized in various aircraft systems.
- Entertainment – vibrators in gaming controllers and autofocus camera mechanism.
- Water treatments – motor pumps and other equipment’s in water treatments plants for the purification and distribution of water.
- Mining and construction – cranes and conveyor systems also in excavators.
- Space exploration – for satellite orientation and deployment.
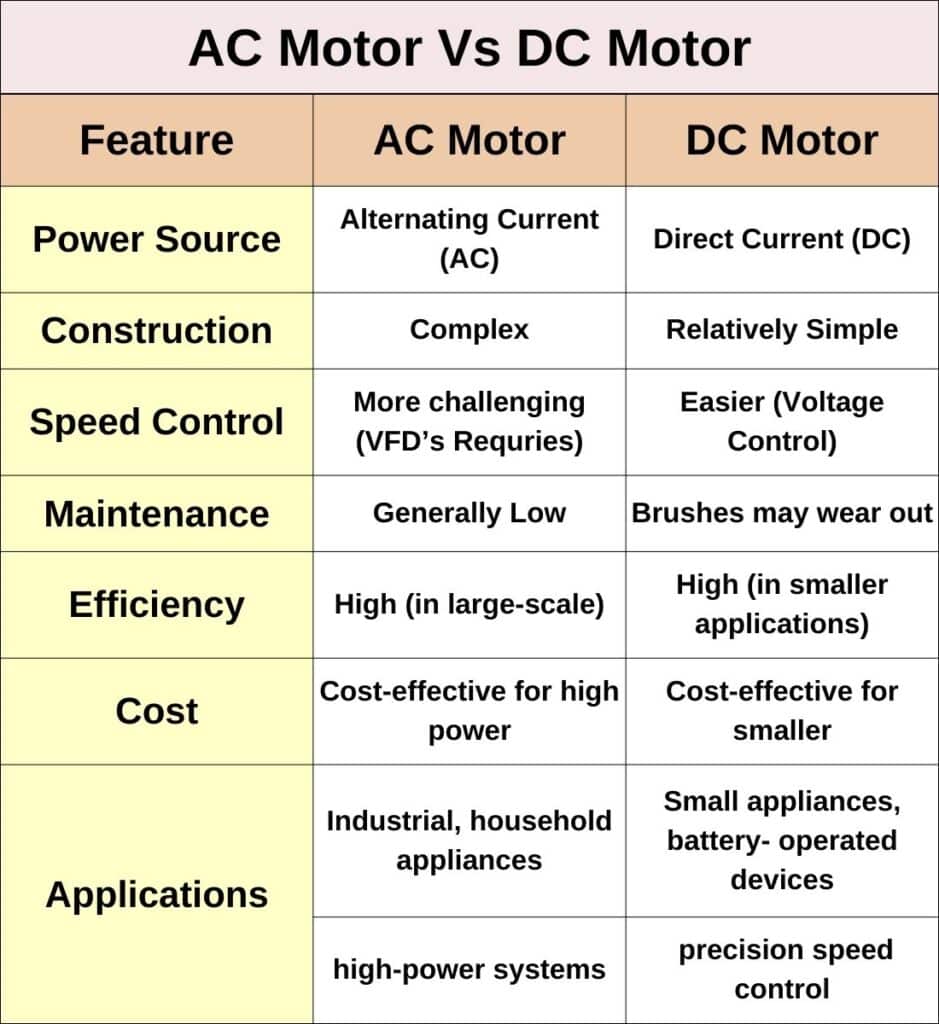
Comparison between AC Motor and DC motor | AC Motor Vs DC motor
So here is the question come what is the difference between AC and DC motor lets clarify them
AC Motor
An AC motors operates on alternating current, where the direction of the electric current periodically changes. This known for their reliability and efficiency. These AC motor such as inductive motors and synchronous motors that are favored for their robust design also requiring less maintenance.
A good factor in AC motor is their speed can control by adjusting the frequency of the AC power supply. Often facilitated by Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs). Their cost effectiveness and efficiency make them suitable for high-power tasks.
DC Motors
On another hand DC Motor rely on direct current with a continuous flow of electric charge in one direction. They have a special characteristic if we adjust the applied voltage then we can control the speed of motor.
Brushless DC motor offering improved efficiency and reduced maintenance due to the absence of brushes and commutator.
formulas of Electrical motor
power of motor formula
the power of a motor can be calculated using the formula
P = V * I
Where,
P is the power watts (W)
V is the voltage volts (V)
I is the current in amps (A)
Torque of motor formula
The Torque of motor can be calculated by
T = Kt * I
T is the torque in newton-meter (Nm)
Kt is the motor torque constant in Nm/A
I is the current flow through the motor in Amperes (A)
Efficiency of electrical motor formula
Efficiency tells us how effectively the motor converts electrical energy (Pin) into Mechanical energy (Pout).
ɳ = (Pout / Pin) * 100 %)
where,
ɳ (eta): is efficiency, expressed as a percentage
Pout (Power out): that give the mechanical output of the motor that will measure in watts.
Pin (Power in): electrical power input to the motor it is also in watts.
Efficiency of motor depending on several factors but generally they range from 75% to 90%.
what is the power factor of a motor?
the power factor of a motor is a measure of how efficiently it converts electrical power into mechanical work. It ranges from 0 to 1 with being ideal efficiency, remember this point
Note: low power factor indicates wastage of energy
Advantages of Electrical Motor
- High efficiency in converting electrical energy to mechanical energy
- Versatility for various applications and industries
- Precise control of speed and torque
- Minimum maintenance
- Wide range of available sizes and power ratings
- Cost-effective
- Compatible with automation and control systems
Disadvantages of Electric Motor
Here are some Disadvantages of Electric Motor
- Initial high cost
- Dependence on a stable power supply
- Wear and tear that required maintenance
- Generation of heat during operation
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q. What are the 3 types of motor?
Ans: here are the three primary types of motor
AC motor (Alternating Motor)
DC Motor (Direct Motor)
Synchronous Motor
Q. What is RPM in electrical motor?
Ans: RPM Or revolutions per Minute in a motor refers to the speed at which the motor shaft rotates in one minute. Formula of RPM
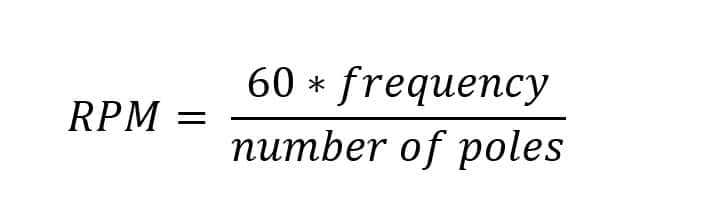
Here,
Frequency is the power supply frequency in hertz (Hz)
Numbers of poles is the number of magnetic poles in the motor
Q. What is a torque of motor?
Ans: torque in a motor is the rotational force it produces it indicating its ability to perform mechanical work.
Q. What is in the stator?
Ans: the stator of an electric motor contains stationary coil or windings that generate the magnetic field required for motor operation.
Also Read:
image source:
Fleming left hand rule- byjus.com
Construction of Electric Motor diagram- www.researchgate.net
Follow to the blog ETechSpark.com for more articles on electrical engineering, electronic and tech updates.
please leave your question in the comment section, give us your valuable feedback.
