Definition of Zener Diode
A Zener diode is a tiny semiconductor device like the PN junction diode but normally operated in the reverse biased conditions. It has the ability to lock a consistent voltage drop when a certain ‘Zener voltage’ is hit in reverse bias.
At this point it conducts current in the reverse direction while maintaining a nearly constant voltage drop across its terminals. This characterises making it more suitable for voltage regulation and protection against voltage spikes.
In this blog post, we will investigate the basics of Zener diode, their characteristics, and their applications.
What is Zener Diode?
A Zener diode, also known as a voltage reference diode or a breakdown diode is a specially designed diode that operates in the reverse- bias mode.

Unlike the regular diode, the regular diode is primarily used for rectification purposes, but the Zener diode is designed to exploit the phenomenon of Zener breakdown
The Zener breakdown occur when a reverse-bias diode is subjected to a voltage higher than its breakdown voltage, causing the diode to conducting current.
Working Principle of Zener Diode
Let’s dive deeper into the working principles of Zener diodes in a diode essentially a p-n junction diode that is heavily doped to reduce its width, and increases its electrical field.
This process allows to diode that has sustain a high electric field and undergo an avalanche breakdown when a certain reverse voltage is applied.
If the doping concentration is higher or the depilation region become shorter than that reduces the breakdown voltage.
A regular diode that completely block the flow of current in reverse bias but a Zener diode is specifically designed to exhibit controlled breakdown.
You might have question How does this happen?
So, answer is here- well inside a Zener diode there is a narrow depletion region created by the PN junction and this depletion region acts as a barrier to the flow of the current, so whenever the reverse voltage is approaches to the breakdown voltage the electrical field strength across the depletion region becomes strong to cause a phenomenon that’s called as avalanche breakdown or Zener breakdown.
And during this Zener breakdown, the potential barrier within the depletion region breaks down and that will create a path for the current flow in the reverse bias. This can be possible because every semiconductor here diodes have some amount of impurities and that’s intestinally alters its properties.
History of Zener Diodes

The Zener diode was invented by the American physicist clarence Melvin Zener in 1950. He discovered a unique effect in semiconductor junction in 1934. As semiconductor technology improved Zener diodes becomes crucial in electronic finding use in various industrial applications also in modern computer technology.
How does a Zener Diode work in reverse bias?
When a Zener diode is in reverse bias it blocks most of current like a regular diode until it reaches a certain reverse voltage, known as the Zener voltage. At this voltage the diode starts conducting in reverse that allowing a controlled amount of current while maintaining a constant voltage across its terminal, which is why it’s great for stabilizing voltage in circuit.
Avalanche Breakdown in Zener Diode
Avalanche breakdown in a Zener diode involves high-energy electrons colliding with atoms that leads to an avalanche -like rapid increases in current while keeping a steady voltage across the diode.
Zener Breakdown in Zener Diode
Zener breakdown in a Zener diode is when the diode is in reverse bias that allows controlled current flow once it hits a specific voltage threshold that known as the Zener voltage.
This characterises enables rather diode to maintain a constant voltage across its terminals that is very crucial for voltage regulations in circuits.
Avalanche Breakdown vs Zener Breakdown
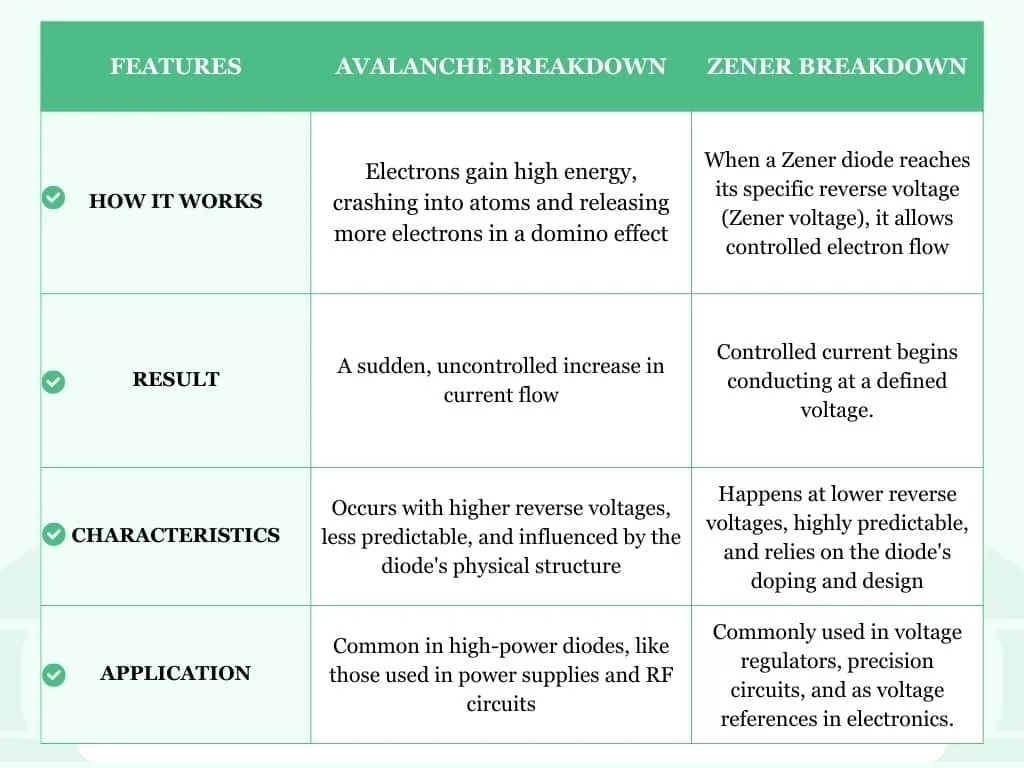
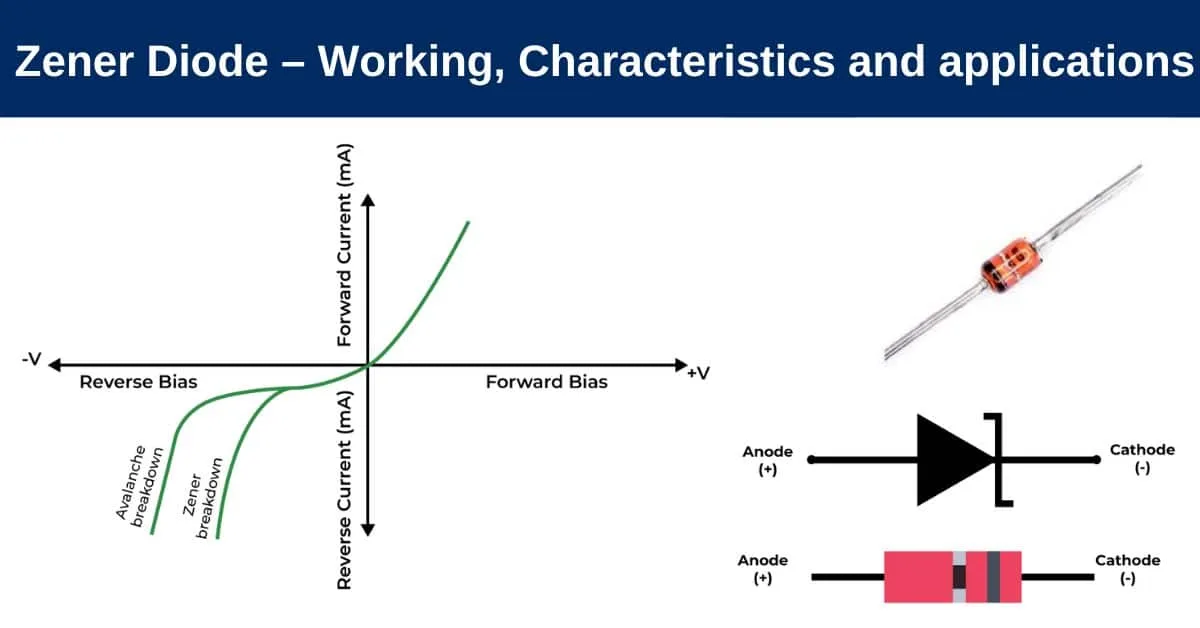
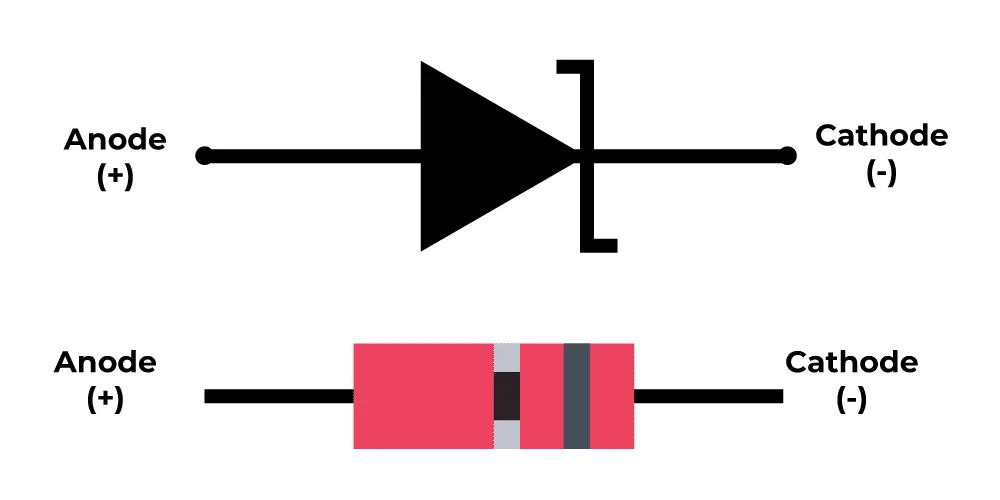
Circuit Symbol of Zener Diode
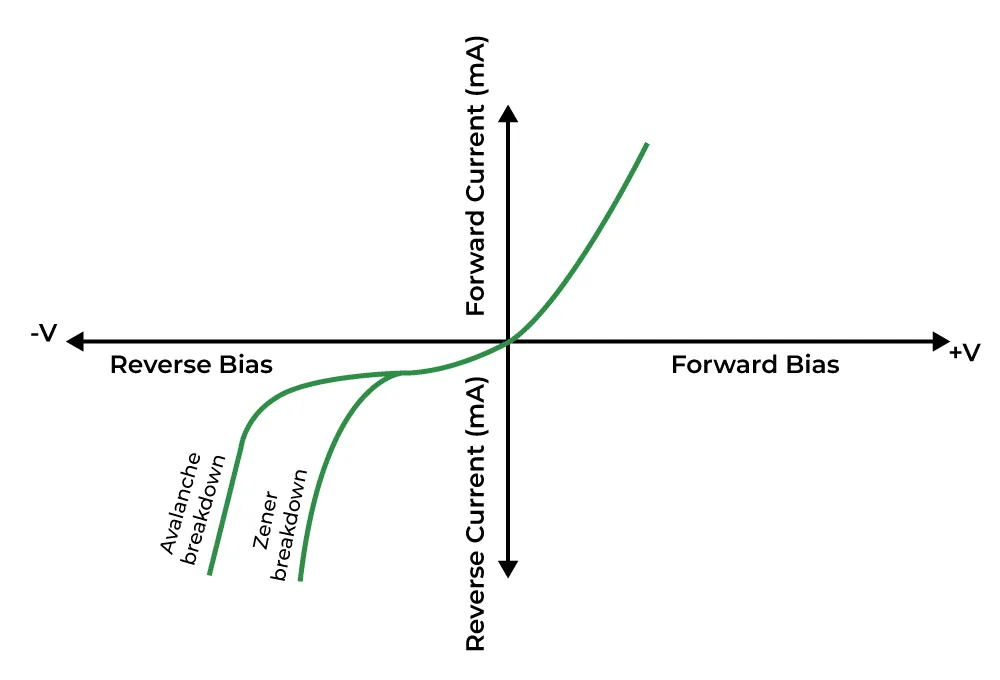
Here is the V-I Characteristics of Zener Diode lets discuss primary both characteristic one by one
Forward Characteristics of Zener Diode
The way a Zener diode behaves in the Forward direction much like a regular diode. You can see this similarity in the voltage-current diagram. When you apply a Forward voltage then it starts conducting electricity similar to the other diodes.
Reverse Characteristics of Zener Diode
When we reverse the voltage a small amount of electricity still passes through due to some heat-generated electrons in the Zener diode. But when we increase this reverse voltage there’s a sudden surge in the electricity passing through at a special point that called the Zener voltage (Vz).
At this point the diode starts working differently that allows more electricity to flow in the reverse direction. This Behaviour helps the Zener diode control voltage even when the current moves in the opposite direction.
Zener Diode Specifications
Zener/Breakdown voltage:
it is similar like the activation voltage for this diode it ranges from 2.4V to 200V even some case up to 1Kv. For the surface mounted once they usually max out at 47V.
Current Iz (max):
this current tells us the how much electricity the diode can be handle, it ranges widely from tiny current like 200microA up to a massive 200 A.
Power Rating:
a power rating can be calculated by multiplying its voltage and the current passing through it. The power rating gives the power limitation of particular diode. So how much power it can handle.
Voltage Tolerance:
a voltage tolerance gives a range of ± 5% within the Zener voltage it can might functioning.
Zener Resistance:
the Zener resistance shown how much is the resistant in the Zener diode when is in working.
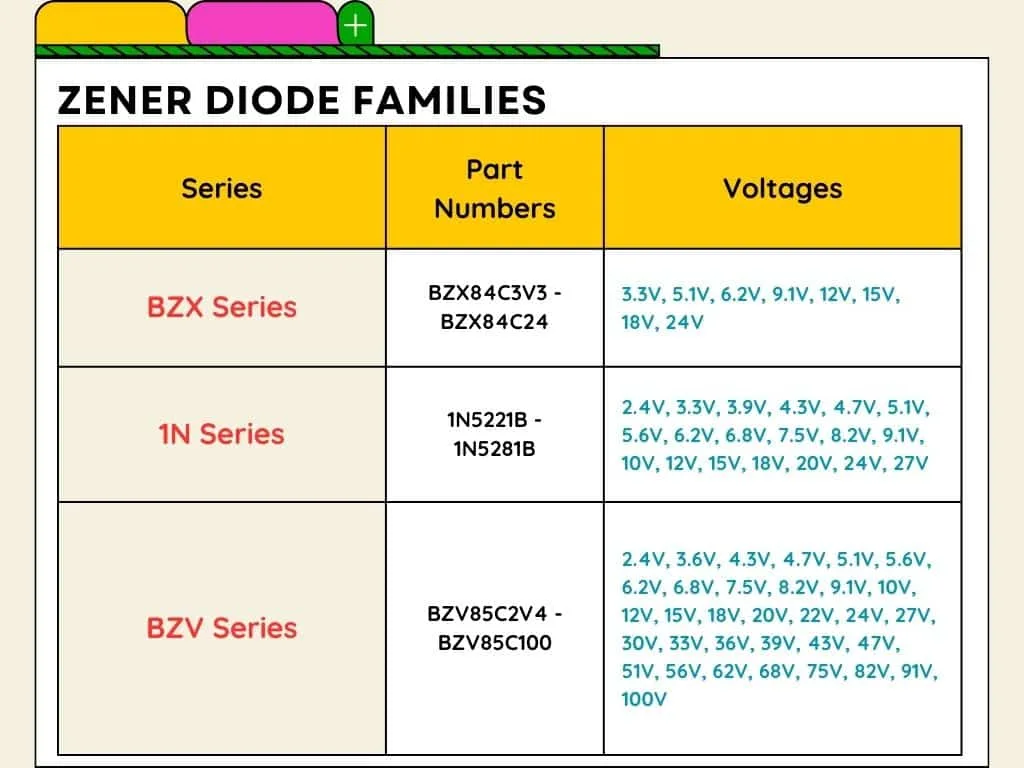
Zener Diode Family
Application of Zener Diode
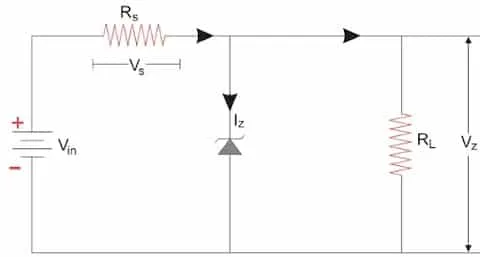
As Voltage Stabilizer
As we understood what is Zener diode and characterises of Zener diode let’s see the
Some Application of Zener Diode – Now here comes some of the interested applications of Zener diode they have a unique characterises that called as voltage regulation. So meaning is that once the Zener breakdown occurs, he voltage across the diode remains relatively constant, regardless of changes in the current flowing through it. Hence this property makes it prefect for voltage stabilizer and regulation applications
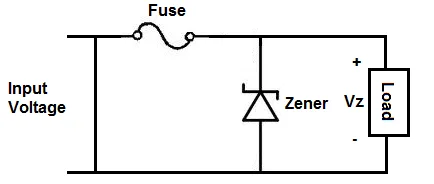
Zener diode in over-voltage protection (For Meter Protection)
Another application of Zener diode is they found in protection devices against in overvoltage. In case the voltage across circuit exceeded the Zener breakdown voltage the diode starts conducting effectively” clamping” or limit the voltage to the breakdown voltage. this saves your circuit from overvoltage damages some case from overvoltage burning.
Zener diode in clipping circuits
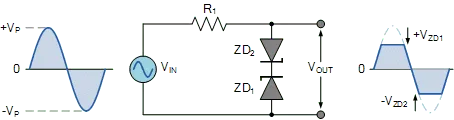
In clipping circuit, a Zener diode is act as a voltage controller. They simply monitor the voltage flowing through a circuit, in condition when the voltage is gone too high so they step in to ensure that it stays below a specific limit that’s has been set.
What is the difference between Zener diode and a normal diode?
| Aspect | Normal Diode | Zener Diode |
|---|---|---|
| Forward Bias | Allows current | Allows current |
| Reverse Bias | Blocks current | Blocks current |
| Breakdown Behaviour | Uncontrolled breakdown | Controlled breakdown at specified voltage (Vz) |
| Application | Rectification, demodulation | Voltage regulation, surge protection |
| Reverse Voltage | Low threshold for breakdown | Higher threshold for controlled breakdown |
| Current Conductance | Higher during breakdown | Controlled, steady during breakdown |
Frequently Asked Questions – FAQs
Q. Is Zener diode AC or DC?
Ans: a Zener diode work in both AC as well as DC circuits to regulate voltage by conducting when a certain reverse voltage (Zener Voltage) is reached so that means Zener diode can work for both (AC and Dc).
Q. How do you test a Zener diode?
Ans: For testing a Zener Diode we need to follow the several steps as below-
Firstly, we need a multimeter and set it to the diode test mode
- Set the multimeter: we need to turn on the multimeter and set it to the diode test mode.
- Identify anode and cathode: for testing the Zener diode we have to identify the anode and cathode terminals of the diode. Usually, the cathode side has band.
- Test Forward Bias: place the multimeter’s positive lead (Red) on the anode side and negative lead to (black) on cathode. We should get a reading in one direction, that indicating the forward bias voltage drop (around 0.5 to 0.7 volts)
- Test Reverse Bias: now we have to swap the multimeter leads, place the positive lead on the cathode and negative lead to anode.
If the diode is fully functional then there should be no reading (or a very high resistance) until the Zener diode is reached.
Note: Ensure the diode is isolated from circuit during testing for accurate results.
Q. Can I use Zener diode instead of normal diode?
Ans: No, both diodes are serves differently purposes due to their distinct functionalities
Q. Can we distinguish between Zener diode and diode using multimeter?
Ans: Yes, a multimeter can differentiate between a Zener diode and regular diode by observing their Behaviour during reverse bias.
Q. Is Schottky diode and Zener diode same?
Ans: No, Schottky diode and Zener diode are different. While both are types of diodes but they serve distinct purposes.
Read More
VI Characteristics Of Pn Junction Diode- Comprehensive Study
How Freewheeling Diode Work: Easy Explanation
What is P-N junction Theory of semiconductor
Diode Definition, Types of Diodes, V-I Characteristics & Application
Conclusion
To sum up Zener diode are very useful components in electronic. With their voltage regulation and overvoltage protection capabilities includes various applications from power supplies to precision measurement of circuits.
Follow to the blog ETechSpark.com for more articles on electrical engineering, electronic and tech updates.
please leave your question in the comment section, give us your valuable feedback.